Çağlayan Demirci . Personal Page
cademirci
I will take a look to this post if I need to a rare time like now that I need to write Java thread code. I hope it also be helpful for you.
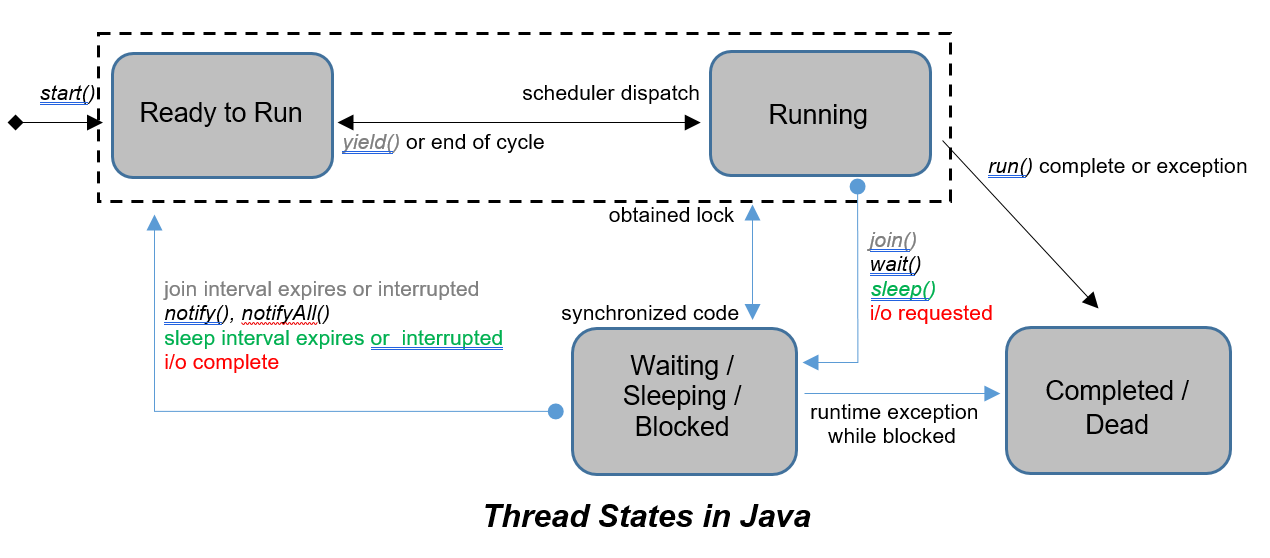
I thought it is a brief time to write a Java Thread note down to my blog, so here we are.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main extends Thread {
public static int columnNumber = 0;
public static double max = 0.0, sum = 0.0;
public static String fileName = "";
public static void main(String[] args) {
fileName = args[0];
String aRow = readFile(fileName).split("\n")[0].replaceAll("\\s{2,}", " ").trim();
// replaceAll("\\s{2,}", " ").trim() is a sweet thing. It erases extra whitespaces
// and converts them into single ones. It is a big simplification for the jobs
// where inappropriate data like absurd text files were given.
int columnCount = aRow.length() - aRow.replaceAll(" ", "").length() + 1;
// that means if there are 3 whitespaces in a row, it has 4 elements
// like "12 9 42 0"
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Main thread = new Main();
thread.start();
while(thread.isAlive()) {
// do nothing, just wait.
}
}
System.out.println("max number: " + trimFloats(max));
System.out.println("sum of the matrix: " + trimFloats(sum));
}
public void run() {
String[] rows = readFile(fileName).split("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < rows.length; i++) {
String currentRow = rows[i].replaceAll("\\s{2,}", " ").trim();
String[] numbersInARow = currentRow.split(" ");
double currentNumber = Double.parseDouble(numbersInARow[columnNumber]);
if (max < currentNumber) {
max = currentNumber;
}
sum += currentNumber;
}
columnNumber++;
}
public static String readFile(String fileName) {
BufferedReader reader;
String fileContent = "", line = "";
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
fileContent += line + "\n";
}
reader.close();
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return fileContent;
}
public static String trimFloats(double number) {
if (number % 1 == 0.0) {
return "" + (int) number;
}
return String.format("%.2f", number);
}
}
This code prints the sum of the numbers in a matrix which is given in a text file and finds the maximum number among them. The point is, it divides the matrix into threads (where thread number is #of columns) then compute them in different forks (threads).
Java threads are dangerous when we want to use attributes or global variables. I want that columnNumber to refer to current column of the matrix with an order 0, then 1, then 2… But if we miss the essence of threads, we may face a chaos like that while CPU is computing a column where suddenly another thread starts before the interpreter sees the columnNumber++. Such an event comes up with computing the same columns at the same time.
In other -simple- words: it is not certain that java goes exactly “0 1 2” (we want this), or like “0 1 1”, “1 2 2”.
In order to avoid that, we can simply add isAlive() method in an empty loop like below.
while (thread.isAlive()) {
// do nothing, just wait.
}
Additionally, this is also related to the answer of why do we prefer modern non-blocking (by default) systems like NodeJS or how does threads work in such systems. This is the topic of an another article.